Sustainability in video processing and streaming encompasses a range of practices aimed at reducing the environmental impact associated with the creation, distribution, and consumption of digital video content. As society becomes increasingly reliant on digital media for entertainment, education, and communication, it’s essential to address the environmental footprint of these activities. From data centers powering video processing to the energy consumption of streaming devices, various aspects of the video ecosystem contribute to carbon emissions and resource depletion.
Efficient Video Processing
With Ateme’s market leading position for video processing, our commitment to sustainability is reflected in our innovative video compression techniques. A prime example is our recently introduced Gen 7 STREAM encoding engine. This advanced engine not only delivers superior video quality at lower bitrates for H.264 and HEVC, but also increases processing density, enabling more channels to be encoded on a single server without compromising video quality. Fewer servers results in lower power consumption and reduced carbon footprint.

Our Emmy-winning Ateme Quality Index combined with the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize video compression, allows us to construct ABR ladders more efficiently. These techniques reduce the number of variants and/or lower bitrates for each variant, leading up to 50% less storage space and reduced CDN bandwidth usage.
Additionally, our ongoing research into next-generation compression technologies such as AV1 and VVC aims to further enhance compression efficiency, achieving even greater reductions in data consumption and associated carbon emissions. To learn more about these advances in compression efficiency, read our blog posts about VVC and AV1.
Streaming Innovations
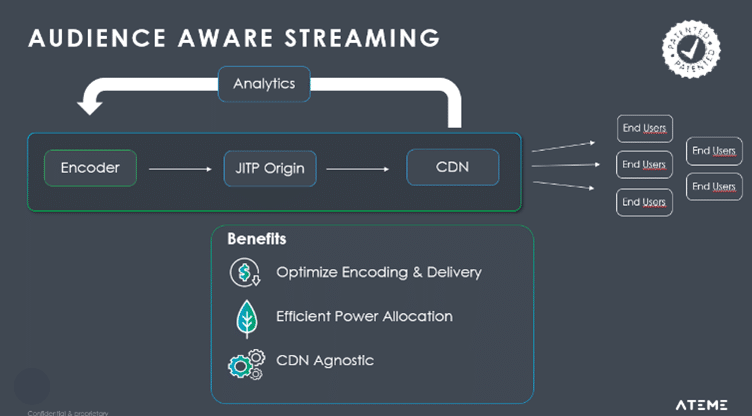
Audience Aware Streaming (or AI Streaming) is another area of Ateme’s sustainability-related innovations. Unlike broadcast, where content is distributed without any knowledge of who is watching or the audience size, streaming delivery provides a detailed data about the viewers, their devices, and delivered profiles.
With this feedback loop and real-time data analysis, we can adapt the encoding process to eliminate lightly- watched profiles, reducing compute and associate power consumption. Additionally, we can HEVC profile when there are enough HEVC capable players, justifying the additional compute. This adaptation reduces CDN resources required to deliver to large audiences the same high-quality experience at a lower bitrate.
Getting More for Less
Another key area of focus is the energy consumption of data centers where video processing occurs. These facilities house thousands of servers and networking equipment that require significant amounts of electricity to operate. By optimizing algorithms and hardware, companies can reduce the computational resources needed for video encoding, decoding, and transcoding, thereby lowering energy consumption and carbon emissions.
In addition to the video processing improvements discussed earlier, Ateme has recently increased the egress performance of the NEA Live origin/packager by over 300%. Similarly, we have increased the NEA CDN edge cache egress to over 500 Gbps. These enhancements result in fewer servers needed to achieve the same level of performance, thereby saving both cost and power.
Ateme CSR Efforts
Sustainability plays a key role in Ateme’s Corporate Social Responsibility efforts. Ateme’s CSR strategy is divided into three main pillars: environmental, social, and governance, under the themes “We care about our planet,” “We care about our people,” and “We care about our ecosystem.” Beyond product innovation efforts to reduce the carbon footprint, Ateme is working to optimize energy consumption in its operations and has adopted teleworking across all group sites.
Ateme is committed to contributing to the global effort to limit the temperature rise to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, in compliance with the Paris Agreement. To this end, Ateme committed to the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) in 2022 by setting specific targets for reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. This commitment includes a reduction in absolute Scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions by 42% by 2030 (compared to 2020, the Group’s base year) and the measurement and reduction of Scope 3 emissions.
Summary
Sustainability in video processing and streaming is a multifaceted issue that requires collaboration and innovation across the industry. By optimizing energy efficiency in its operations, enhancing video compression techniques, and improving performance in video processing and delivery networks, Ateme is leading the video streaming industry in minimizing its environmental footprint and contributing to a more sustainable future.

